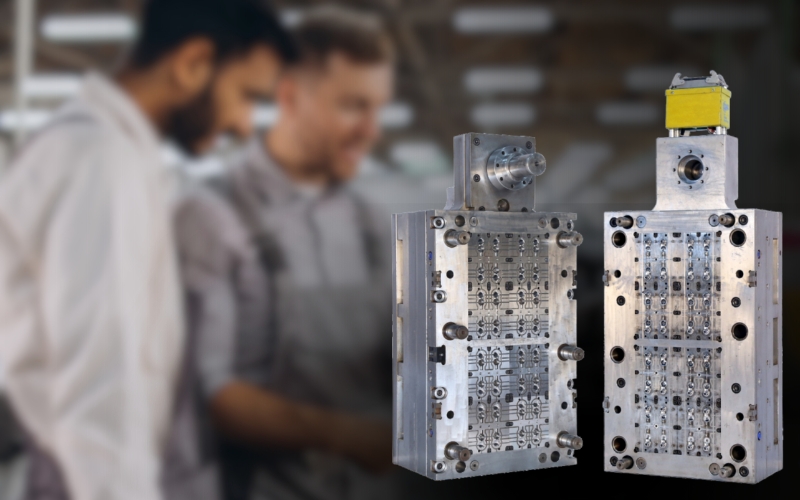
When we think about the everyday products we use—from food containers to cosmetics packaging—we rarely consider the intricate processes behind their creation. One of the most significant contributors to modern manufacturing is molding, which shapes raw materials into usable forms. If you’re part of industries like FMCG, Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals, or even household care, understanding mold and molding processes can give you a competitive edge.
Understanding Mold
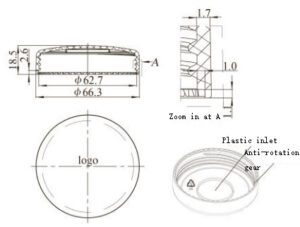
Mold, or mould in British English, is essentially a hollow container used to give shape to liquid or pliable raw material. It comes in various sizes and complexities, depending on the application. Once the material hardens or sets inside the mold, it retains the shape of the cavity.
The Molding Process
The molding process is versatile and can involve several techniques. At its core, the process involves pouring or injecting a liquid material into a mold where it cools and solidifies. This method is widely used in manufacturing everything from automotive parts to household items.
Molding in Casting
Casting is one of the oldest molding methods, primarily used in metalworking. In this technique, molten metal is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. The mold is then broken away to reveal a metal casting. This process is indispensable in industries requiring high-strength components, like aerospace and automotive sectors.
Mold Design
Designing a mold is a meticulous task requiring expertise and advanced software tools. The design must account for factors like material flow, cooling time, and the ease of removing the finished product. Poor design can lead to defects, making this an area where investing in quality pays off.
Molding in Manufacturing
Molding isn’t limited to just casting metals; it extends to various manufacturing processes involving plastics, resins, and even ceramics. The choice of molding process depends on the material and the desired properties of the final product.
Plastic Molding
Plastic molding is particularly crucial in the FMCG, cosmetics, and household care industries. This technique involves heating plastic until it’s pliable and then injecting it into a mold. Once cooled, the plastic retains the mold’s shape.
The Plastic Bottle Cap Molding Process
One of the most common applications of plastic molding is in the production of bottle caps. This process starts with feeding plastic pellets into a heated barrel. The molten plastic is then injected into a mold cavity. After cooling, the mold opens to eject the finished cap.
Plastic Cap Molding Materials
Choosing the right material is vital for ensuring the durability and functionality of plastic caps. Common materials include:
- Polyethylene (PE): Known for its flexibility and resilience.
- Polypropylene (PP): Offers excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications.
- Polystyrene (PS): Used for its rigidity and clarity.
Types of Plastic Cap Molding Materials
Different types of plastic materials are used for various applications:
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
- Common in milk jugs and detergent bottles.
- Offers strength and impact resistance.
- Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE):
- Used for squeeze bottles.
- Provides flexibility and transparency.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS):
- Applied in durable goods like appliance housings and protective gear.
- Known for its toughness and high impact resistance.
Types of Plastic Bottle Cap Molds
Various molds are designed to produce different kinds of bottle caps:
- Compression Molds:
- Ideal for high-volume production.
- Known for reducing waste and energy consumption.
- Injection Molds:
- Used for producing complex shapes.
- Offers high precision and consistency.
-
Industries That Need Plastic Bottle Cap Molds
Several industries rely heavily on plastic bottle cap molds:
- FMCG Industry:
- Essential for packaging consumer goods such as beverages and cleaning products.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care Industry:
- Used in packaging lotions, shampoos, and other personal care items.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Critical for ensuring the safe packaging of medications and health supplements.
- Food and Beverage Industry:
- Ensures the secure sealing of food containers and bottles.
Conclusion
Understanding mold and molding processes is essential for industries aiming to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. From the intricacies of mold design to the specifics of plastic bottle cap production, mastering these processes can lead to improved product quality and operational efficiency. For businesses looking to elevate their manufacturing game, investing in advanced molding techniques and materials is a step in the right direction.

